| Cat No. |
Variants |
Size |
Buy |
Images |
|
FM01 |
Collecting River System : Collecting river system consists of a network of tributaries in the headwater region. V-shaped valleys, interlocking spurs, rapids, waterfalls and gorges are features associated with it. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM02 |
Transporting River System : Main trunk stream system of water and sediment movement from collecting system towards dispersing system. Meanders, oxbow lakes and levees are features associated with it. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM03 |
Ice Sheet and Icebergs : An ice sheet is a mass of glacial land ice extending more than 50,000 square kilometers. An ice shelf is the floating extension of the ice sheets. The primary mechanism of mass loss from ice shelves is iceberg calving. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM04 |
Convergent Plate Boundaries : Convergent plate boundaries, also known as destructive plate boundaries are zones where lithospheric plates collide. Magma is generated at subduction zones. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
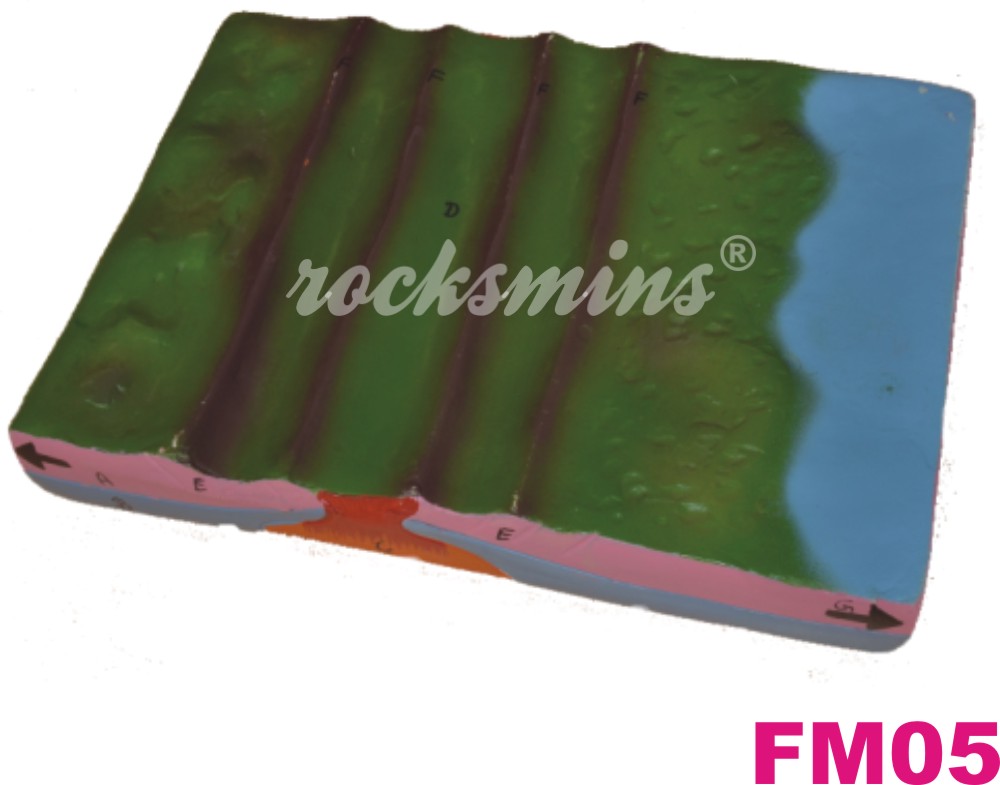
FM05 |
Divergent Plate Boundaries : Divergent plate boundaries, also known as constructive plate boundaries are zones where lithospheric plates drift from one another. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM06 |
Transform Plate Boundaries : Transform plate boundaries move horizontally past each other on strike-slip faults. Lithosphere is neither created nor destroyed. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
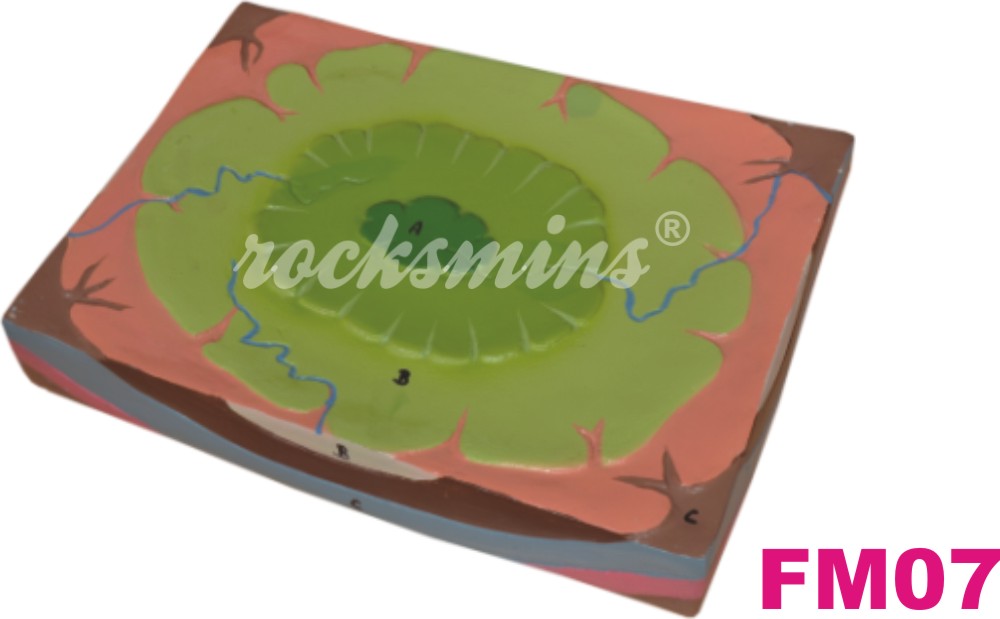
FM07 |
Structural Basin : A structural basin is a large-scale structural depression of rock strata formed by tectonic warping of previously flat lying strata. The exposed strata in a basin are progressively younger from outside-in, with the youngest rocks in the center. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM08 |
Plateau : A plateau is an area of highland, usually consisting of relatively flat terrain. The essential criteria for plateaus are low relative relief and some altitude. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
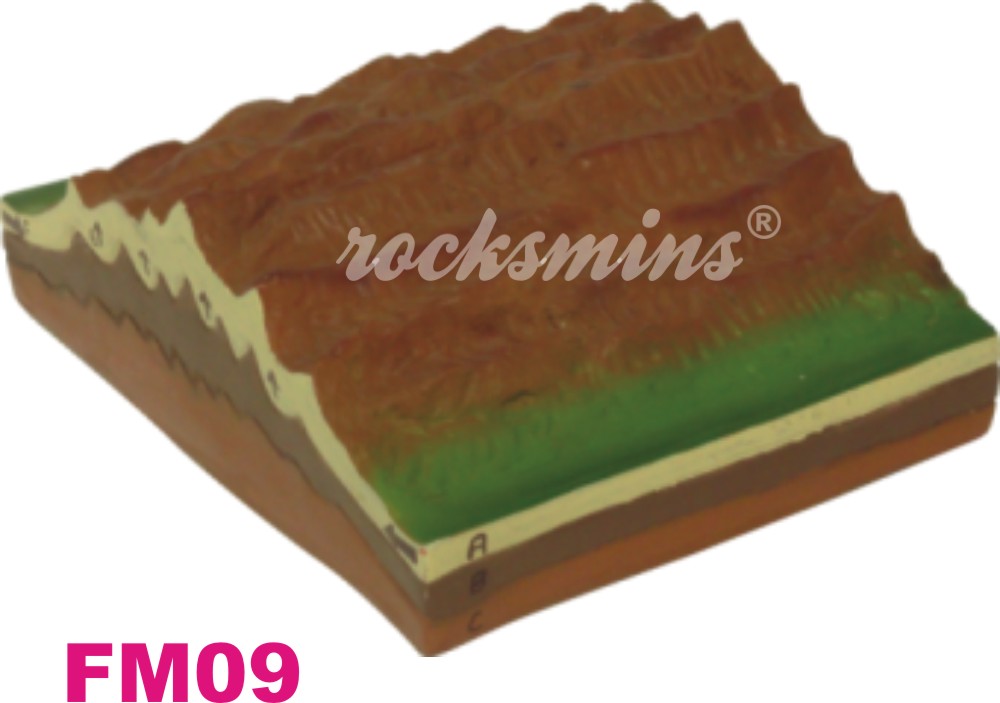
FM09 |
Fold Mountains : Mountains formed mainly by the effects of uplift and folding on layers within the upper part of the Earth's crust. Fold Mountains are usually formed from sedimentary rocks. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM10 |
Normal Fault : In normal fault, the hanging wall block moves down relative to the footwall block. Normal faults are associated with crustal tension. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
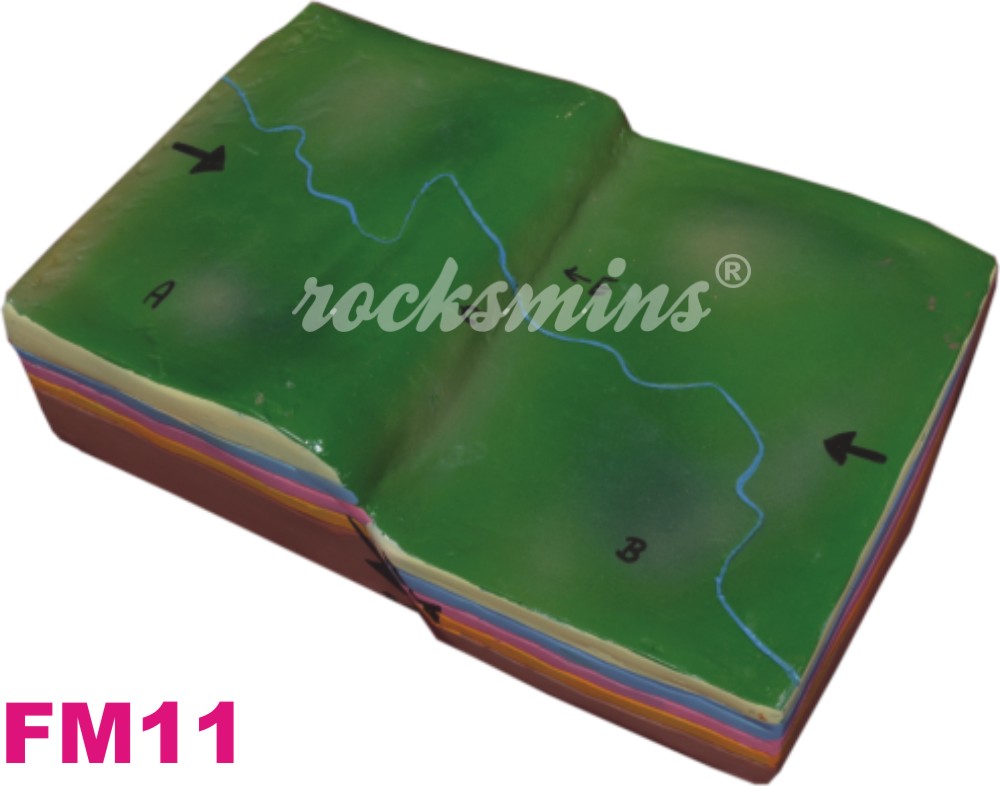
FM11 |
Reverse Fault : In reverse fault, the hanging wall block moves up relative to the footwall block. Reverse faults are associated with the crustal compressions. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
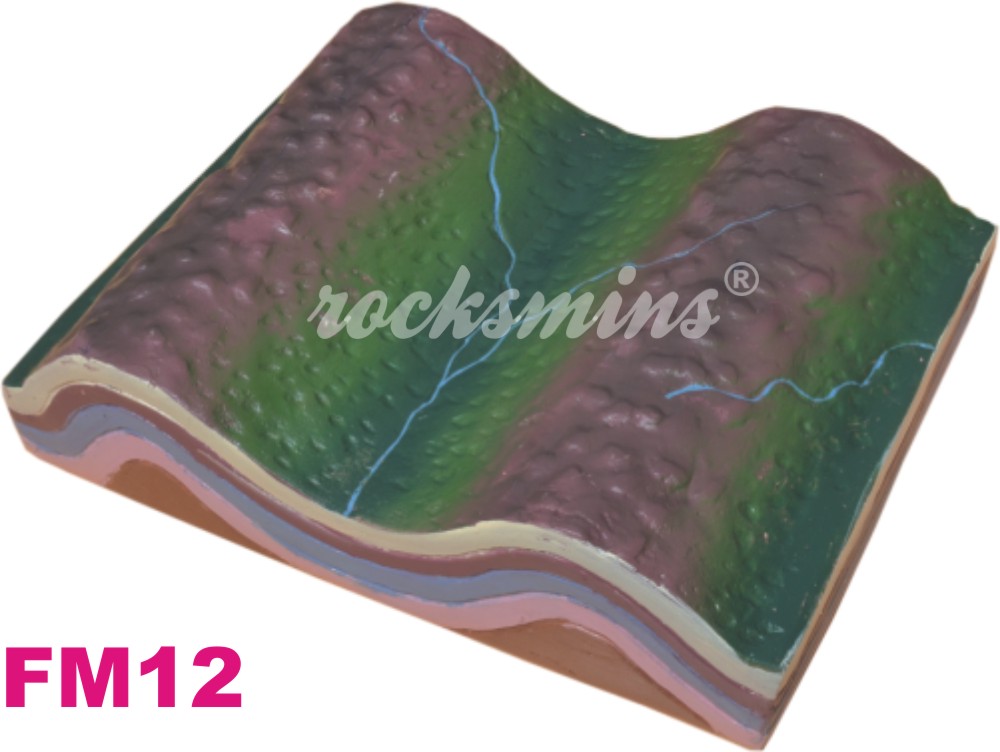
FM12 |
Anticlines and Synclines : Anticlines and synclines are folded rock layers formed in sections of the crust that are undergoing compression. Anticlines are arch shaped and synclines are trough shaped. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM13 |
Horsts and Grabens : Horsts and grabens are the regions that lie between normal faults. A horst represents a block pushed upward by the faulting, and a graben is a block that has dropped due to the faulting. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM14 |
Groundwater : Water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. Ground water can be obtained by drilling or digging wells. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM15 |
Sand Dunes - Barchans : A barchan dune is an arc-shaped sand ridge, comprising well-sorted sand. Barchans are the commonest types of dunes occurring in sandy deserts. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|
|
FM16 |
Archipelago : An archipelago is a chain or cluster of islands. Archipelagos may be found isolated in bodies of water or neighboring a large land mass. |
25x35 cm |
-
|

|